Our kidneys help in removing all the waste from our body, all the while playing more vital functions, like controlling the dilution of blood ( fluid balance ), regulating various electrolytes in the blood stream and maintaining the acidity of the blood. also regulates blood pressure.
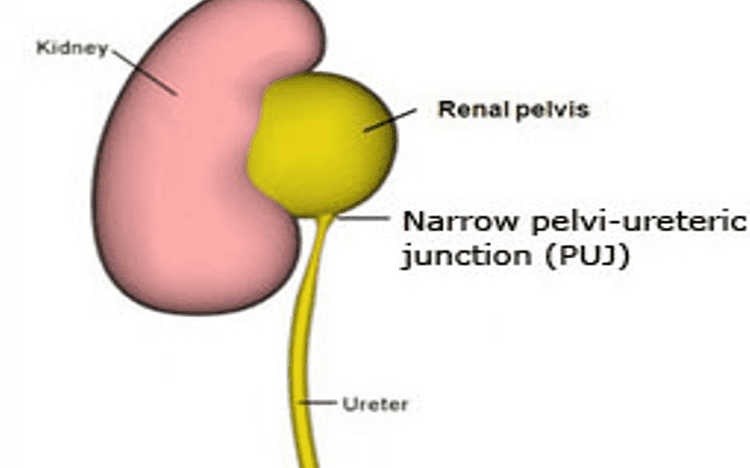
PUJ obstruction refers to the narrowing of a junction, obstructing the flow of urine from the kidney to the ureter. This condition affects 1 person in every 1000 group of people. This disease is more common in men than in women.
PUJ Obstruction can be:
• intrinsic – the blockage occurs inside, e.g. due to stenosis (a narrowing of the passage).
• extrinsic – the blockage is caused by an external factor putting pressure on the PUJ, such as an extra blood vessel crossing over the ureter.
In most cases, PUJ obstruction is diagnosed before birth, because it causes a dilatation in the urinary tract, which can be seen on prenatal scans. However, it is possible to get a PUJ obstruction later in childhood or even in adulthood, in which case symptoms can include a sharp flank pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting; urinary tract infections; or swelling in the abdomen.
Usually, ultrasound is suggested for diagnosis, which shows swallowing of the kidney.
If the diagnosis is still not confirmed, other options include an MRI of the urinary tract or a retrograde pyelogram to see the urinary tract anatomy and urine drainage more clearly.
PUJ obstruction is treated by means of a procedure called pyloplasty. The procedure can be performed with an open incision or via laparoscopy, with or without robotic assistance.