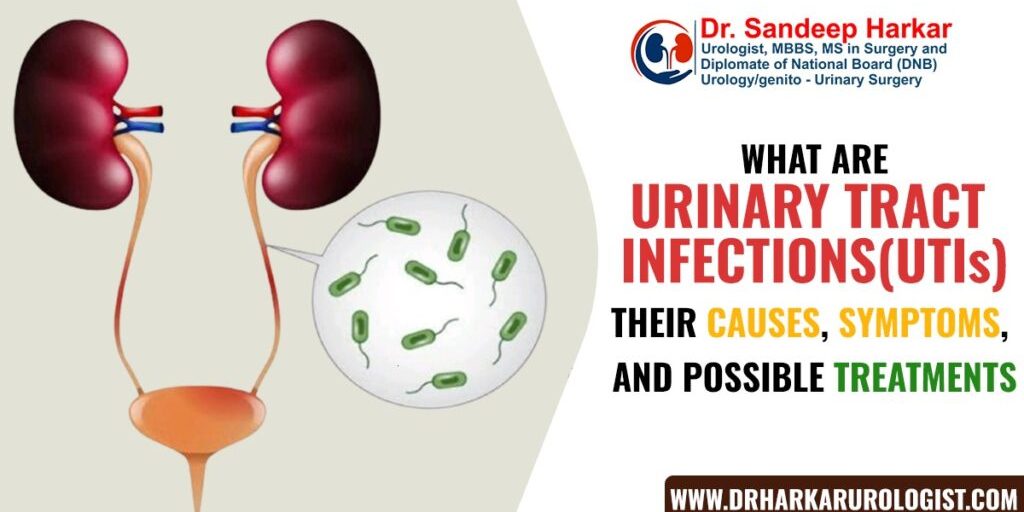
Urinary Tract Infections or UTIs are infections caused in any part of the urinary tract. It is a common health issue that affects millions of people every year. Women are more likely to get this infection in comparison to men. Urine is the byproduct of the blood purification process done by our kidneys. Kidneys create urine when they filter the blood and remove the waste products with excess water from the blood. Urine contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It does not contain bacteria, viruses, or fungi. The urinary tract infection develops when germs, most often bacteria prominently E. Coli bacteria enter the urethra which is a tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, and cause infection to the other parts of your urinary system. Urethra is the exit for the urine, but it is also the entrance of the bacteria to get into the urinary tract system. This issue is caused more in women than men as in women the urethra is shorter in comparison to men. Bacteria is present at the point where urine exits the body, so in women, bacteria have to travel shorter distance in comparison to men.
What are the Possible Causes of Urinary Tract Infection?
Germs mainly bacteria cause Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs). They enter the Urinary Tract System through the urethra from where the urine exits the body. When urine exits the body bacteria follow the same urethra to enter the urinary tract and start multiplying themselves causing infection and thus may infect the bladder. This infection can also travel up from the bladder using the same path, followed by urine leaving the body, through the ureter, and could cause infection to your kidneys also.
What are the Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)?
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) causes inflammation in your Urinary Tract System. This inflammation may cause the following problems in your body:
• Pain While Urination
• Pain within the flank which is the area between your pelvis and ribs, abdomen, pelvic area, or lower back.
• Cloudy, foul-smelling urine.
• Frequent Urination
• Urgency & occasionally urge- incontinence
• Fever
Who is at a Greater Risk of Developing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)?
In comparison to men, women are more likely to develop Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs). This heath issue occurs nearly 4 times in women than in men. In women, the urethra is short and straight making it easy for the germs more often bacteria to travel into the Urinary Tract System. The reason behind women getting more Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) than men is also the fact that in women the urethra is closer to the rectum, which carries solid waste from the body, and thus bacteria especially E. Coli bacteria get into the body through the urethra, and cause infection in the balder. The Urinary Tract System of the women is structured so that after sexual contact, the bacteria present near the vagina get into the urethra and thus travel into the bladder to cause infection. Pregnant women are also more likely to get Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) as various kinds so infections could occur to them and their baby.
How To Diagnose Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)?
Your doctor will ask about the symptoms you are getting when you consult them for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs). He may also ask about your medical history and do a physical exam. Other tests may also include:
Urinalysis: In this test, the urine is tested in the laboratory to see the signs of a UTI including various cells and chemicals, such as red blood cells and white blood cells and germs (like bacteria), or a lot of protein.
In case UTIs occur frequently, your doctor may suggest you do other tests to know whether your urinary tract is normal or not. These tests are:
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP): In this test, a series of X-rays of the kidney, ureters, and bladder are done. In this test, a contrast dye is injected into a vein. It can show how your renal and urinary system handles fluid waste. This helps to find problems in your urinary tract.
Cystoscopy: Within this test, a thin, flexible tube and a viewing device like a camera are inserted into the urethra to know the condition of the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract.
Kidney and Bladder Ultrasound: It is an imaging test in which high-frequency sound waves are used to make images of the bladder and the kidneys on a computer screen. This test is used to know the size and shape of the bladder and the kidneys and to know about any possible blockage or abnormalities within the urinary tract.
What is the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Treatments of Urinary Tract Infections includes:
• Antibiotics
• Medicines to give relief from pain
• Heat in the form of a heating pad to give relief from pain
Precautions To Prevent Occurrence of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
• Drink cranberry juice. Take Vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables like oranges, strawberries, kiwifruit, tomatoes, and green leafy vegetables and especially cranberry to limit the UTI infection. Intake of these fruits and vegetables limits the growth of bacteria by acidifying the urine.
• Drink plenty of water
• Whenever you feel an urgency to urinate do not wait and urinate.
• Women need to wipe from front to back to keep the bacteria away.
• Wear only cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothes. This will help the urethra keep dry. Within Nylon underwear and tight-fitting clothes, the moisture gets trapped helping bacteria growth.